Overview
Cat #:
Size:
10 mg
Lot:
F105SM0110
Alternative Name Agon®, Plendil®, Renedil®
Lyophilized Powder yes
Source Synthetic
MW: 384.25
Purity: >99%.
Effective concentration 1-10 μM.
Chemical name 4-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3,5 pyridinedicarboxylic acid ethyl methyl ester.
Molecular formula C18H19Cl2NO4.
CAS No.: 72509-76-3
Activity Felodipine is a dihydropyridine that acts as L-type, voltage-gated Ca2+ channel blocker and is used in the clinic to treat hypertension1,2.
References-Activity
- Furukawa, T. et al. (1999) J.P.E.T. 291, 464.
- Furukawa, T. et al. (2005) J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 45, 241.
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility DMSO. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to four weeks at 4°C or three months at -20°C.
Our bioassay
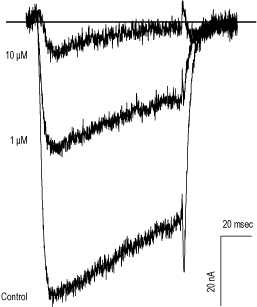 Alomone Labs Felodipine blocks L-type Ca2+ currents in Xenopus oocytes.Superimposed current traces of L-type channels (CaV1.2+α2δ1+β1a), before and during applications of 1 and 10 μM Felodipine (#F-105) as indicated on the left. Holding potential was -100 mV and currents were elicited every 10 seconds by 100 ms steps to +10 mV.
Alomone Labs Felodipine blocks L-type Ca2+ currents in Xenopus oocytes.Superimposed current traces of L-type channels (CaV1.2+α2δ1+β1a), before and during applications of 1 and 10 μM Felodipine (#F-105) as indicated on the left. Holding potential was -100 mV and currents were elicited every 10 seconds by 100 ms steps to +10 mV.
Target L-type Ca2+ channels
Lyophilized Powder
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 30/03/2021
Specifications
Citations
Citations

