Overview
Cat #:
Size:
1 g
Lot:
M206SM011
Alternative Name Albistat, Andergin, Aflorix, Conofite
Lyophilized Powder yes
Source Synthetic
MW: 479.1
Purity: >97%.
Effective concentration 1-100 µM.
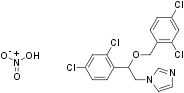
Chemical name 1-[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)methoxy]ethyl]imidazole;nitric acid.
Molecular formula C18H15Cl4N3O4.
CAS No.: 22832-87-7
PubChem CID 68553
Activity Miconazole blocks hERG in HEK transfected cells as well as KV1.3 and KV1.51.
References-Activity
- Kikuchi, K. et al. (2005) Br. J. Pharmacol. 144, 840.
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility 100 mM in DMSO. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to four weeks at 4°C or three months at -20°C.
Our bioassay
 Alomone Labs Miconazole nitrate Blocks KV11.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of KV11.1 current inhibition by 10 and 50 µM Miconazole nitrate (#M-206). Currents were elicited by two 200 ms steps: to +40 mV and then to -40 mV (HP -100mV, every 10s, demonstrated above current traces in B). B. Superimposed example traces of current responses before and during perfusion of 10 and 50 µM Miconazole nitrate, as indicated.
Alomone Labs Miconazole nitrate Blocks KV11.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes.A. Time course of KV11.1 current inhibition by 10 and 50 µM Miconazole nitrate (#M-206). Currents were elicited by two 200 ms steps: to +40 mV and then to -40 mV (HP -100mV, every 10s, demonstrated above current traces in B). B. Superimposed example traces of current responses before and during perfusion of 10 and 50 µM Miconazole nitrate, as indicated.
Target KV11.1, KV1.3, KV1.5 channels
Lyophilized Powder
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 30/03/2021
Specifications
Citations
Citations