Overview
- Synthetic peptide mapping to the 3rd extracellular loop of human KCa3.1 (Accession O15554).

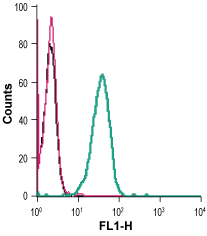 Cell surface detection of KCNN4 in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of KCNN4 in live intact human THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + mouse IgM isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ALM-051-F), (2.5 µg). Cell surface detection of KCNN4 in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
Cell surface detection of KCNN4 in live intact mouse J774 macrophage cells:___ Cells.
___ Cells + mouse IgM isotype control-FITC.
___ Cells + Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ALM-051-F), (5 µg).
- Ghanshani, S. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 37137.
- Hoffman, J.F. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 7366.
KCa3.1 (KCNN4, SK4) is a member of the Ca2+ activated K+ channel family that shares the characteristic of being activated by intracellular Ca2+. The channel has an intermediate conductance, is voltage insensitive and is activated by Ca2+ in the submicromolar range. The channel has a similar topology to that of KV channels, that is, six transmembrane domains and intracellular N- and C-termini.
KCa3.1 is widely expressed in epithelial, endothelial and cells of hematopoietic origin. In erythrocytes (red blood cells) it has been identified as the molecular correlate of the so-called Gardos channel.
The functional role of the channel is to set the cell membrane potential at negative values so as to aid in the electrochemical transport of other ions such as Cl- and Ca2+. Indeed, KCa3.1 has a key role in sustaining the Ca2+ influx in activated T lymphocytes and in regulating Cl- secretion from colon epithelium. Therefore, specific blockers of the KCa3.1 channel have been proposed for the treatment of several diseases including autoimmune diseases, secretory diarrhea and sickle cell anemia.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular) Antibody (#ALM-051) is a highly specific monoclonal antibody directed against an epitope of the human channel. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and indirect flow cytometry applications. It has been designed to recognize KCNN4 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Mouse Anti-KCNN4 (KCa3.1, SK4) (extracellular)-FITC Antibody (#ALM-051-F) is directly conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). The antibody can be used in immunofluorescent applications such as direct live cell flow cytometry.
Applications
Citations
- Rat BMSCs.
Jia, X. et al. (2020) J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24, 3739.
