Overview
- Omura, S. et al. (1986) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 39, 1211.
- Tomoda, H. et al. (1987) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 17, 595.
Protect from light.
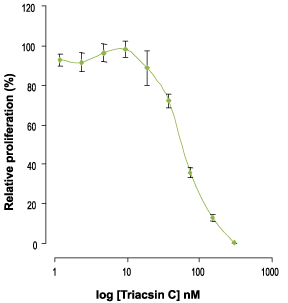 Alomone Labs Triacsin C inhibits the proliferation of 3T3-L1 cells.Cells were treated with different concentrations of Triacsin C (#T-750) for 3 days. The number of live cells was measured by XTT cell proliferation assay kit, normalized to the control (100%) and plotted against the drug concentration.
Alomone Labs Triacsin C inhibits the proliferation of 3T3-L1 cells.Cells were treated with different concentrations of Triacsin C (#T-750) for 3 days. The number of live cells was measured by XTT cell proliferation assay kit, normalized to the control (100%) and plotted against the drug concentration.
- Yoshida, K. et al. (1982) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 35, 151.
- Omura, S. et al. (1986) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 39, 1211.
- Tomoda, H. et al. (1987) Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 17, 595.
- Tomoda, H. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 4214.
- Hartman, E.J. et al. (1989) Prostaglandins 37, 655.
Triacsin C is a fungal metabolite from Streptomyces aureofaciens1 which almost completely inhibits de novo synthesis of triacylglycerol and phospholipid.2,3 This compound specifically inhibits the activity of long chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1 and 4 (IC50~8µM) but has no effect on the activity of acyl-CoA synthetase 5, in intact cells and in cell lysates. Inhibition of these enzymes causes a decrease in the cellular levels of acyl-CoA precursors for lipid synthesis activity, cell proliferation and lipid transformation.4 Kinetic analysis indicates that inhibition of acyl-CoA synthetase by Triacsin C is not competitive with respect to the two substrates of acyl-CoA synthetase (ATP and coenzyme A), but is competitive with respect to long-chain fatty acids. The N-hydroxytriazene moiety of Triacsin C has been suggested to be essential for the inhibitory activity against acyl-CoA synthetase.2-4
Triacsin C arrests the metabolism of arachidonic acid by inhibition of arachidonoyl-CoA synthetase thus interfering in the production of prostaglandins and in the regulation of blood pressure.5
Triacsin C (#T-750) is a highly pure, natural, and biologically active compound.
Applications
Citations
- Narita, T. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 25469.
- Araujo, J.R. et al. (2013) J. Nutr. Biochem. 24, 1741.