Overview
- Peptide (C)KLEESLREQAEKEGSALSVR, corresponding to amino acid residues 356-375 of rat Kir4.1 (Accession P49655). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysates (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP), (1:800).
Western blot analysis of rat brain membranes (lanes 1 and 4), mouse brain membranes (lanes 2 and 5) and human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell lysates (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP), (1:800).
4-6. Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody, preincubated with Kir4.1/KCNJ10 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC035).
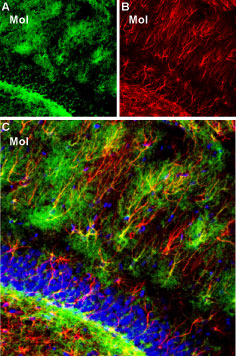 Expression of Kir4.1 in rat hippocampal dentate gyrusImmunohistochemical staining of rat frozen brain sections using Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP), (1:300). A. Kir4.1 staining (green) reveals Kir4.1 clusters in the molecular layer (Mol). B. The same section was stained with mouse anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), (red) showing astrocyte profiles. C. Merge of Kir4.1 and GFAP images reveals colocalization on some branches of astrocytic fibers. In addition, Kir4.1 is expressed in the fine ramification of astrocytic fibers, thus creating a “halo-like” cloud around the GFAP astrocytic outline. DAPI (blue) counterstain reveals the outline of the dentate granule layer.
Expression of Kir4.1 in rat hippocampal dentate gyrusImmunohistochemical staining of rat frozen brain sections using Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP), (1:300). A. Kir4.1 staining (green) reveals Kir4.1 clusters in the molecular layer (Mol). B. The same section was stained with mouse anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), (red) showing astrocyte profiles. C. Merge of Kir4.1 and GFAP images reveals colocalization on some branches of astrocytic fibers. In addition, Kir4.1 is expressed in the fine ramification of astrocytic fibers, thus creating a “halo-like” cloud around the GFAP astrocytic outline. DAPI (blue) counterstain reveals the outline of the dentate granule layer.
 Expression of Kir4.1 in human U-87 MG glioblastoma cell lineImmunocytochemical staining of fixed and permeabilized U-87 MG cells using Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP), (1:100) followed by goat anti-guinea pig-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Cell nuclei were visualized using Hoechst 33342 (blue).
Expression of Kir4.1 in human U-87 MG glioblastoma cell lineImmunocytochemical staining of fixed and permeabilized U-87 MG cells using Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP), (1:100) followed by goat anti-guinea pig-AlexaFluor-488 secondary antibody (green). Cell nuclei were visualized using Hoechst 33342 (blue).
- Takumi, T. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, 16339.
- Higashi, K. et al. (2001) Am. J. Physiol. 281, C922.
- Butt, A.M. et al. (2006) J. Cell Mol. Med. 10, 33.
Kir4.1 is a member of the family of inward rectifying K+ channels. The family includes 15 members that are structurally and functionally different from the voltage-dependent K+ channels.
The family’s topology consists of two transmembrane domains that flank a single and highly conserved pore region with intracellular N- and C-termini. As is the case for the voltage-dependent K+ channels the functional unit for the Kir channels is composed of four subunits that can assemble as either homo or heteromers.
Kir channels are characterized by a K+ efflux that is limited by depolarizing membrane potentials thus making them essential for controlling resting membrane potential and K+ homeostasis.
Kir4.1 is a member of the Kir4 subfamily that includes one other member: Kir4.2. Kir4.1 can co-assemble with Kir4.2 but also with other Kir channels such as Kir2.1 and Kir5.1.
The Kir4 subfamily has been classified as weak rectifiers with intermediate conductance.
Kir4.1, encoded by KCNJ10, is mainly expressed in brain, specifically in glia cells, but also in retina, ear and kidney1,2.
It has been proposed that Kir4.1 has an essential role in glial K+ buffering, a process that re-uptakes the K+ released during neuronal activity into the intracellular interstitial space. Loss of Kir4.1 causes retinal defects and loss of endochoclear potential3.
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP) is a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize Kir4.1 potassium channel from human, rat, and mouse samples. The antigen used to immunize guinea pigs is the same as Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035) raised in rabbit. Our line of guinea pig antibodies enables more flexibility with our products such as multiplex staining studies, immunoprecipitation, etc.

Multiplex staining of Kir4.1 and α1-Syntrophin in rat fornixImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using Guinea pig Anti-Kir4.1 (KCNJ10) Antibody (#APC-035-GP), (1:400) and Anti-α1-Syntrophin (SNTA1) Antibody (#APZ-021), (1:300). A. Kir4.1 staining (red) appears in blood vessel profiles (arrows) in the fornix. B. Syntrophin alpha 1 staining in the same section (green) appears in several elements including blood vessels (arrows). C. Merge of the two images reveals partial co-localization of Kir4.1 and syntrophin alpha 1 in hilar cells. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Applications
Citations
- Western blot and immunohistochemistry of mouse kidney. Tested in mice with conditional Kir4.1 knockout in the distal convoluted tubule.
Zhang, D-D. et al. (2023) JCI Insight 8, e165987.
- Mouse brain lysate.
Mendez-Gonzalez, M.P. et al. (2020) Brain Sci. 10, 72.
- Rat DRG sections.
Xiang, H. et al. (2018) J. Neurosci. Res. 96, 436. - Mouse brain sections. Also tested in Kir4.1-/- mice.
Brasko, C. et al. (2016) Brain Struct. Funct. 222, 41. - Mouse DRG sections (1:1000).
Rajasekhar, P. et al. (2015) J. Biol. Chem. 290, 29051.
- Rat DRG sections.
Xiang, H. et al. (2018) J. Neurosci. Res. 96, 436.
