Overview
- Peptide (C)SNQLQSSEDEPAFVSK, corresponding to amino acid residues 454-469 of rat KV4.2 (Accession Q63881). Intracellular, C-terminus.

 Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 4), rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human U-87 MG glioblastoma cell lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:500).
Western blot analysis of mouse brain lysate (lanes 1 and 4), rat brain lysate (lanes 2 and 5) and human U-87 MG glioblastoma cell lysate (lanes 3 and 6):1-3. Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:500).
4-6. Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody, preincubated with Kv4.2 Blocking Peptide (#BLP-PC023).
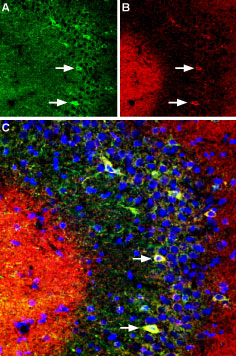 Multiplex staining of DPP6 and KV4.2 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:400) and Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:1000). A. DPP6 (green) is expressed in the CA3 rat hippocampal region. B. KV4.2 (red) is expressed in the same region. C. Merge of the two images demonstrates partial colocalization in neurons of the CA3 region (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue).
Multiplex staining of DPP6 and KV4.2 in rat hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of immersion-fixed, free floating rat brain frozen sections using rabbit Anti-DPP6 (extracellular) Antibody (#APC-146), (1:400) and Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:1000). A. DPP6 (green) is expressed in the CA3 rat hippocampal region. B. KV4.2 (red) is expressed in the same region. C. Merge of the two images demonstrates partial colocalization in neurons of the CA3 region (arrows). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Expression of KV4.2 in mouse CA1 hippocampal regionImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:400), followed by biotinylated donkey anti-guinea pig antibody and Streptavidin-Cy3. KV4.2 staining (red) appears in stratum oriens (SOR) and stratum radiatum (SR). Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue).
Expression of KV4.2 in mouse CA1 hippocampal regionImmunohistochemical staining of perfusion-fixed frozen mouse brain sections using Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), (1:400), followed by biotinylated donkey anti-guinea pig antibody and Streptavidin-Cy3. KV4.2 staining (red) appears in stratum oriens (SOR) and stratum radiatum (SR). Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue).
- Roberds, S.L. and Tamkun M.M. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 1798.
- Serodio, P. et al. (1994) J. Neurophysiol. 72, 1516.
- Guo, W. et al. (2002) Circ. Res. 90, 586.
- Escoubas, P. et al. (2002) Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 48.
KV4.2 is a voltage-dependent K+ channel that belongs to the Shal channel subfamily and includes two other members: KV4.1 and KV4.3.1
KV4.2 possesses the signature structure of the voltage-dependent K+ channels: six membrane-spanning domains with intracellular N and C termini. As with other members of the voltage-gated K+ channel superfamily, the functional channel is a tetramer that can be composed of more than one member of the Shal subfamily, i.e. heterotetramers of KV4.1 and KV4.3.
The KV4 channels are characterized by activation at subthreshold membrane potentials, inactivate rapidly and recover from inactivation quickly compared with other voltage-dependent K+ channels. This type of current is known as transient A-type K+ currents. For example, depolarization-activated K+ currents in rat neostriatal cholinergic interneurons are predominantly of the A-type and attributable to coexpression of KV4.2 and KV4.1 subunits.2
The biophysical properties of the KV4.2 subunit can be modified by its association with auxiliary β subunits such as the KChIP family that increase KV4.2 current densities and accelerates both the inactivation and the recovery time.
KV4.2 is also highly expressed in the heart where together with KV4.3 underlie the fast inactivating and recovering cardiac transient outward current Ito.3
Several toxins from spider venoms are potent blockers (affecting the channels in the nanomolar range) of KV4.2 channels. Among these the most potent and selective are Stromatoxin-1 (#STS-350), (1.2nM), Phrixotoxin-1 (#STP-700), (5 nM), Phrixotoxin-2 (#STP-710), (34 nM) and Heteropodatoxin-2 (#STH-340), (100 nM).4
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Alomone Labs is pleased to offer a highly specific antibody directed against an epitope of rat KV4.2 channel. Guinea pig Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023-GP), raised in guinea pig, can be used in western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize KV4.2 from mouse, rat and human samples. The antigen used to immunize guinea pigs is the same as Anti-KV4.2 Antibody (#APC-023) raised in rabbit. Our line of guinea pig antibodies enables more flexibility with our products such as multiplex staining studies, immunoprecipitation, etc.
