Overview
Cat #:
S-350
Alternative Name Antibiotic AM-2282
Lyophilized Powder yes
Origin Streptomyces staurosporeus.
Source Natural
MW: 466
Purity: >98%
Effective concentration 10 nM - 1 µM.
Chemical name [9S-(9a,10b,11b,13a)]-2,3,10,11,12,13-Hexahydro-10- meth oxy-9-methyl-11-(methylamino)-9,13-epoxy-1H,9H-diindolo [1,2,3- gh:3',2',1'-lm]pyrrolo[3,4-j][1,7]benzodiazonin-1-one.
Molecular formula C28H26N4O3.
CAS No.: 62996-74-1
Activity Staurosporine potently inhibits a variety of kinases including PKC (IC50 = 0.7 nM), PKA (IC50 = 7 nM) and PKG (IC50 = 8.5 nM)1,2. It also inhibits CaMK (IC50 = 20 nM)3 and MLCK (IC50 = 1.3 nM)1,2. In addition, Staurosporine can act as an agonist promoting neurite outgrowth4. At higher concentrations, Staurosporine induces apoptosis5.
References-Activity
- Tamaoki, T. et al. (1986) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 135, 397.
- Matsumoto, H. et al. (1989) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 158, 105.
- Yanagihara, N. et al. (1991) J. Neurochem. 56, 294.
- Rasouly, D. et al. (1992) Mol. Pharmacol. 42, 35.
- Wang, X. et al. (1996) EMBO J. 15, 1012.
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility DMSO or methanol. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to one week at 4°C or three months at -20°C.
Protect from light.
Protect from light.
Our bioassay
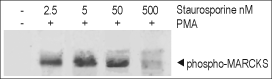 Alomone Labs Staurosporine inhibits MARCKS phosphorylation via PKC in C6 glioma cells.Cells were grown to 70% confluence and then serum starved for 18 h. The cells were preincubated for 30 min with different concentrations of Staurosporine (#S-350) and stimulated with 2 µM PMA (#P-800) for 30 min. Cell proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with antiphospho (ser)-MARCKS (myristoylated alanin-rich protein kinase C substrate).
Alomone Labs Staurosporine inhibits MARCKS phosphorylation via PKC in C6 glioma cells.Cells were grown to 70% confluence and then serum starved for 18 h. The cells were preincubated for 30 min with different concentrations of Staurosporine (#S-350) and stimulated with 2 µM PMA (#P-800) for 30 min. Cell proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with antiphospho (ser)-MARCKS (myristoylated alanin-rich protein kinase C substrate).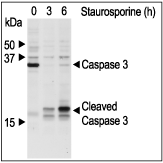 Alomone Labs Staurosporine induces apoptosis in Jurkat cells.Cells were grown to 70% confluency then 2 µM Staurosporine (#S-350) or vehicle were added for 3 or 6 hours. At the end of the incubation period, cell proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with Caspase 3 and cleaved Caspase 3 specific antibodies.
Alomone Labs Staurosporine induces apoptosis in Jurkat cells.Cells were grown to 70% confluency then 2 µM Staurosporine (#S-350) or vehicle were added for 3 or 6 hours. At the end of the incubation period, cell proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with Caspase 3 and cleaved Caspase 3 specific antibodies.
References - Scientific background
- Ruegg U.T. and Burgess, G.M. (1989) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 10, 218.
- Tamaoki, T. et al. (1986) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 135, 397.
- Matsumoto, H. et al. (1989) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 158, 105.
- Couldwell, W.T. et al. (1994) FEBS Lett. 345, 43.
- Bruno, S. et al. (1992) Cancer Res. 52, 470.
- Vitale, M.L. et al. (1992) Neuroscience 51, 463.
- Hoffman, R. and Newlands, E.S. (1991) Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 28, 102.
- Begemann, M. et al. (1998) Anticancer Res. 18, 3139.
- Oh, Y.J. et al. (1997) Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 51, 133.
- Hou, S.T. et al. (2000) J. Neurochem. 75, 91.
- Rasouly, D. et al. (1992) Mol. Pharmacol. 42, 35.
- Yao, R. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18261.
- Kruman, I. et al. (1998) J. Neurosci. Res. 51, 293.
- Jacobsen, M.D. et al. (1996) J. Cell Biol. 133, 1041.
- Posmantur, R. et al. (1997) J. Neurochem. 68, 2328.
- Chakravarthy, B.R. et al. (1999) J. Neurochem. 72, 933.
Scientific background
Staurosporine is a member of the K252a family of fungal alkaloids produce by Streptomyces staurospores.1,2 It is one of the most potent, cell permeable protein kinase inhibitors, and it is often used to study the involvement of protein kinases in signal transduction pathways (IC50 0.7-20 nM).3-10
In pheochromocytoma PC12 cells, neuroblastoma and brain primary culture Staurosporine is a functional neurotropins agonist promoting neurite outgrowth (EC50 = 50 nM).11-12 At concentrations higher then 0.5 mM, Staurosporine generates apoptosis in several different cell types or induces G1 and G2 phase arrest in normal cells.13-16
Target PKA, PKC, PKG
Lyophilized Powder
Staurosporine (#S-350) is a highly pure, natural, and biologically active compound.
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 07/05/2024
Applications
Citations
Citations

