Overview
- Guillemare, E. et al. (1992) Biochemistry 31, 12463.
- Grissmer, S. et. al. (1994) Mol. Pharmacol. 45, 1227.
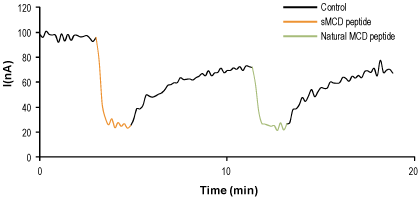 Alomone Labs MCD peptide inhibits KV1.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of KV1.2 current inhibition by 200 nM of MCD peptide (#STM-250) (orange) compared to natural MCD peptide (green) recorded at -20 mV. The toxins were perfused to the recording bath for a period of 100 sec. Holding potential was -80 mV and test pulses to 60 mV were delivered for 150 msec.
Alomone Labs MCD peptide inhibits KV1.2 channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of KV1.2 current inhibition by 200 nM of MCD peptide (#STM-250) (orange) compared to natural MCD peptide (green) recorded at -20 mV. The toxins were perfused to the recording bath for a period of 100 sec. Holding potential was -80 mV and test pulses to 60 mV were delivered for 150 msec.
- Jentsch, J. and Mucke, H.W. (1977) Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 9, 78.
- Schwartz, L.B. et al. (1979) J. Immunol. 123, 1445.
- Aniksztejn, L. et al. (1990) Neuroscience 35, 63.
- Guillemare, E. et al. (1992) Biochemistry 31, 12463.
- Grissmer, S. et. al. (1994) Mol. Pharmacol. 45, 1227.
- Southan, A.P. and Owen, D.G. (1997) British J. Pharmacol. 122, 335.
- Mourre, C. et al. (1997) Brain Res. 762, 223.
MCD peptide (Mast Cell Degranulating Peptide) is a 22 amino acid peptidyl toxin isolated from Apis mellifera bee venom1. MCD peptide induces histamine release from mast cells2 and release of glutamate in CA1 region of rat hippocampus in dose-dependent manner3.
MCD peptide was shown to block KV1.2 channels in Xenopus oocytes4 and to inhibit KV1.1 (IC50 490 nM) and KV1.2 (IC50 440 nM) expressed in cell lines while having no effect on KV1.3, KV1.5 and KV3.15. In accordance, MCD peptide (6.4 µM) enhances the magnitude of field potentials in CA1 region as recorded in hippocampal slices6 and induces epileptiform seizures and brain damage after intracerebroventricular injection of 200 pM in rats7.
MCD peptide (#STM-250) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.

