Overview
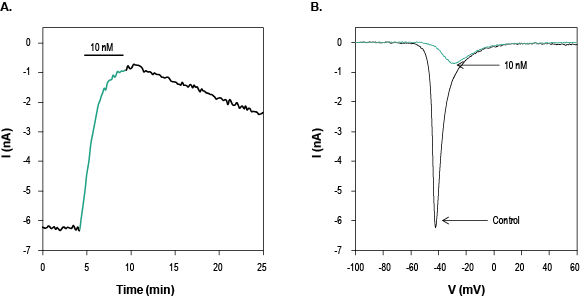 Alomone Labs Jingzhaotoxin-V inhibits NaV1.7 channels heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells.NaV1.7 currents were elicited by 30 ms voltage ramp from the holding potential of -100 mV to +60 mV, applied every 10 sec using whole-cell voltage clamp technique. A. Time course of NaV1.7 current amplitude changes before (black) and during (green) application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V (#STJ-050) indicated by the horizontal bar. B. Superimposed example current traces of NaV1.7 currents before (black) and during (green) 200 sec application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V, as indicated.
Alomone Labs Jingzhaotoxin-V inhibits NaV1.7 channels heterologously expressed in HEK293 cells.NaV1.7 currents were elicited by 30 ms voltage ramp from the holding potential of -100 mV to +60 mV, applied every 10 sec using whole-cell voltage clamp technique. A. Time course of NaV1.7 current amplitude changes before (black) and during (green) application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V (#STJ-050) indicated by the horizontal bar. B. Superimposed example current traces of NaV1.7 currents before (black) and during (green) 200 sec application of 10 nM Jingzhaotoxin-V, as indicated.
- Zeng, X.Z. et al. (2007) Toxicon 49, 388.
- Chen, J. et al. (2008) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 2431.
Jingzhaotoxin-V is a 29 amino acid peptidyl toxin isolated from the Chilobrachys jingzhao (Chinese earth tiger tarantula) spider1. It significantly inhibits tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) and tetrodotoxin-sensitive (TTX-S) Na+ channels in adult rat DRG neurons as well as KV4.2 K+ channels expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes1.
It was found that Jingzhaotoxin-V alters the gating properties of Na+ channels by shifting the activation curves to the depolarizing direction and the inactivation curves to the hyperpolarizing direction1. The findings related to this peptide further reinforced the viewpoint that gating-modifier toxins can alter the voltage-dependent gating through the lipid membrane partitioning1.
Jingzhaotoxin-V (#STJ-050) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active peptide toxin.