Overview
- Edwards, G. et al. (1994) Br. J. Pharmacol. 113, 1538.
- Sellers, A.G. and Ashford, L.M.J. (1994) Br. J. Pharmacol. 113, 659.
- Ningaraj, N.S. et al. (2002) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301, 838.
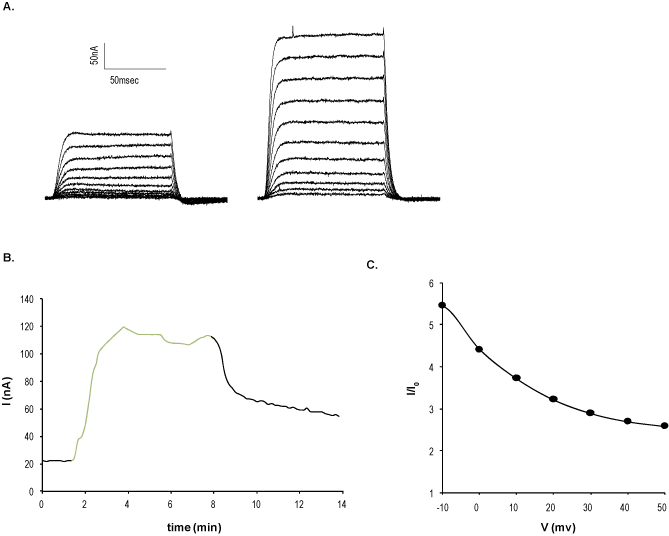 Alomone Labs NS-1619 enhances KCa1.1 currents in Xenopus oocytes.A. Families of KCa1.1 channel current responses to increasing voltage step stimulation (from -50 mV to + 50 mV), before (left) and during (right) application of 100 μM NS-1619 (#N-105). Currents were elicited by 100 ms voltage step from -100 mV applied every 10 sec. B. Time course of current amplitude at 0 mV before, during application of 100 μM NS-1619 (green) and upon wash, demonstrating the current amplitude enhancement. C. Voltage dependence of KCa1.1 channel activity enhancement.
Alomone Labs NS-1619 enhances KCa1.1 currents in Xenopus oocytes.A. Families of KCa1.1 channel current responses to increasing voltage step stimulation (from -50 mV to + 50 mV), before (left) and during (right) application of 100 μM NS-1619 (#N-105). Currents were elicited by 100 ms voltage step from -100 mV applied every 10 sec. B. Time course of current amplitude at 0 mV before, during application of 100 μM NS-1619 (green) and upon wash, demonstrating the current amplitude enhancement. C. Voltage dependence of KCa1.1 channel activity enhancement.
- Andersson K.E. et al. (2004) Physiol. Rev. 84, 935.
- Heppner, T.J. et al. (1997) Am. J. Physiol. 273, C110.
- Salkoff, L. et al. (2006) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 921.
- Olesen S.P. et al. (1994) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 251, 53.
- Holland M. et al. (1996) Br. J. Pharmacol. 117, 119.
- Macmillan S. et al. (1995) Br. J. Pharmacol. 116, 1656.
- Yamamura H. et al. (2001) Br. J. Pharmacol. 132, 828.
- Han X. et al. (2008) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 375, 205.
- Wrzosek, A. (2014) Cell Calcium 56, 14.
The large conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channels, also known as BKCa, KCa1.1, Slo, or MaxiK, play an important role in modulating nerve and muscle cell contractility and excitability1-3. BK channels are activated by both depolarizing voltages and by an increase in intracellular free Ca2+, thus coupling the membrane potential to intracellular signaling.
NS-1619 is a potent and selective KCa1.1 channel modulator (enhancer)4. It has the potential to modulate cell excitability in neurons and smooth muscle5-7. The effect of relaxation of NS-1619 on the BK channel in smooth muscle cells has an EC50 of 10–30 µM. It is also dose-dependent, resulting in a shift of the activation curve by up to -50 mV towards negative membrane potentials, but fully reversible8.
NS-1619 also modulates intracellular Ca2+ by inhibiting SERCA pumps9.
NS-1619 (#N-105) is a highly pure, synthetic, and biologically active compound.

