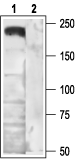
Overview
- Peptide (C)RHHRHRDRDKTSASTPA, corresponding to amino acid residues 851-867 of rat CACNA1B (Accession Q02294). Intracellular loop between domains II and III.
- Transfected tsA201 cells (1:200) (Marangoudakis, S. et al. (2012) J. Neurosci. 32, 10365.).
- Mouse cerebellum (1:100).
- Rat DRGs (1:200).
NCI-H295R human adrenocortical cell line (H295R) (1:100) (Aritomi, S. et al. (2011) Hypertens. Res. 34, 193.).
Voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (CaV channels) are pivotal players in many physiological roles such as secretion, contraction, migration and excitation.1
The voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels are composed of several subunits; α1, β, α2δ and γ. CaV channels were originally divided into six physiological types: L-, N-, P-, Q-, R-, and T-type.
The CaV2.2 (formally named α1B) composes the α1 poreforming subunit for the N-type Ca2+ channel family. They are involved in neurotransmitter release from central neurons, including glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid, acetylcholine, dopamine and noradrenaline.2
The CaV2.2 is expressed preferentially in the central nervous system, where along with CaV2.1, it is responsible for pre-synaptic Ca2+ influx and neurotransmitter release.1,3
The CaV2.2 channel is negatively regulated by many different GPCRs. There are two ways that this is done: either by directly binding Gβγ to the channel or by an indirect mechanism involving second messenger and channel phosphorylation.4
ω-Conotoxin GVIA (#C-300) is a specific blocker of CaV2.2 Ca2+ channels. It specifically blocks N-type CaV channels by binding to the CaV2.2 α1 subunit (α1B) and its action is only partially reversible.5,6
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
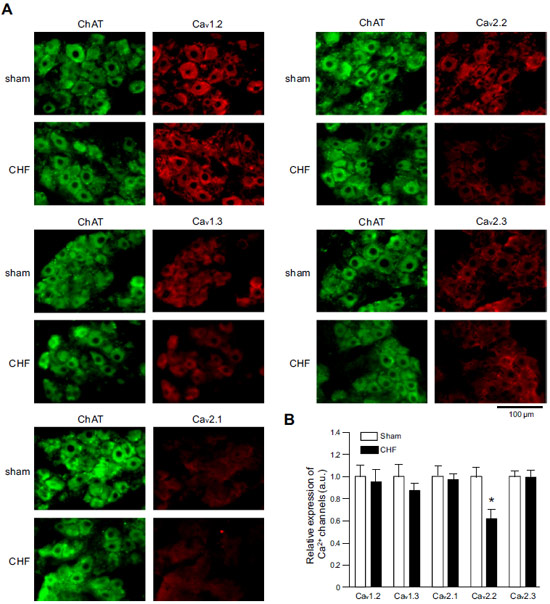 Expression of CaV α subunits in rat ICG.Immunohistochemical staining of rat intracardiac ganglia (ICG) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), Anti-CACNA1A (CaV2.1) Antibody (#ACC-001), Anti-CACNA1B (CaV2.2) Antibody (#ACC-002) and Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). All CaV subtypes are expressed in sham treated rats but N-type CaV channel levels are decreased in CHF rats.Adapted from Tu, H. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.
Expression of CaV α subunits in rat ICG.Immunohistochemical staining of rat intracardiac ganglia (ICG) using Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003), Anti-CaV1.3 (CACNA1D) Antibody (#ACC-005), Anti-CACNA1A (CaV2.1) Antibody (#ACC-001), Anti-CACNA1B (CaV2.2) Antibody (#ACC-002) and Anti-CaV2.3 (CACNA1E) Antibody (#ACC-006). All CaV subtypes are expressed in sham treated rats but N-type CaV channel levels are decreased in CHF rats.Adapted from Tu, H. et al. (2014) with permission of the American Physiological Society.