Overview
- Peptide QPSQDELKDNTTVFTR(C), corresponding to amino acid residues 28-43 of rat GABRA1 (Accession P62813). Extracellular, N-terminus.
 Multiplex staining of CaV1.2 and GABA(A) α1 Receptor in rat and mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of mouse and rat hippocampal dentate gyrus using Guinea pig Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003-GP) and Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG) in the same section. Both CaV1.2 (red) and GABRA1 (green) are detected in neuron-shaped cells (arrows). Staining suggests partial colocalization between CaV1.2 and GABRA1 in a sub-population of rat dentate gyrus neurons. A. Mouse hippocampus. B. Rat hippocampus.
Multiplex staining of CaV1.2 and GABA(A) α1 Receptor in rat and mouse hippocampusImmunohistochemical staining of mouse and rat hippocampal dentate gyrus using Guinea pig Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003-GP) and Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG) in the same section. Both CaV1.2 (red) and GABRA1 (green) are detected in neuron-shaped cells (arrows). Staining suggests partial colocalization between CaV1.2 and GABRA1 in a sub-population of rat dentate gyrus neurons. A. Mouse hippocampus. B. Rat hippocampus. Expression of GABRA1 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat dentate gyrus using Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG) (green). Staining reveals hilar neurons (arrows) and fibers coursing through the granule layer (G). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
Expression of GABRA1 in rat brainImmunohistochemical staining of rat dentate gyrus using Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG) (green). Staining reveals hilar neurons (arrows) and fibers coursing through the granule layer (G). DAPI is used as the counterstain (blue).
- Rat primary hippocampal neurons (Sarto-Jackson, I. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 14201.).
 Expression of GABRA1 in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of GABRA1 in intact living rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG), (1:25), (green). B. Live view of the cell. C. Merge image of A and B.
Expression of GABRA1 in rat PC12 cellsCell surface detection of GABRA1 in intact living rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. A. Extracellular staining of cells using Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG), (1:25), (green). B. Live view of the cell. C. Merge image of A and B.
- Owens, D.F. and Kriegstein, A.R. (2002) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 715.
- Whiting, P.J. (1999) Neurochem. Int. 34, 387.
- Mihic, S.J. and Harris, R.A. (1997) Alcohol Health Res. World 21, 127.
- Neelands, T.R. et al. (1999) J. Neurosci. 19, 7057.
- Fuchs, K. and Celepirovic, N. (2002) J. Neurochem. 82, 1512.
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Its production, release, reuptake, and metabolism all occur in the nervous system.1
The GABA transmitter interacts with two major types of receptors: ionotropic GABAA receptors (GABAAR) and metabotropic receptors (GABABR). GABAARs belong to the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily.2 GABA inhibits the activity of signal-receiving neurons by interacting with the GABAA receptor on these cells.3 Binding of GABA to its GABAA receptor results in conformational changes that open a Cl- channel, producing an increase in membrane conductance that results in inhibition of neural activity.2
GABAARs are heteropentamers, in which all five subunits contribute to pore formation. To date, eight subunit isoforms have been cloned:α, β, γ, δ, ε, π, θ, and ρ.1 Six α subunit isoforms have been found to exist in mammals (α1-α6). In most cases, native GABAA receptors consists of 2α, 2β, and 1δ subunits. The α subunit is the most common and is expressed ubiquitously. It determines the affinities of GABAARs for allosteric ligands.
Each subtype has a unique regional expression in the brain, and individual neurons often express multiple subtypes.4 The α1 subunit is highly expressed in adulthood while the α2 subunit is highly expressed very early in rat brain development. Failure to complete the normal transition between the α-subunits that are highly expressed in early development (α2, α3, and α5) and those expressed in adulthood (α1) is suggested to play a major role in the development of temporal lobe epilepsy.5
Application key:
Species reactivity key:
Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular) Antibody (#AGA-001) is a highly specific antibody directed against an extracellular epitope of the rat protein. The antibody can be used in western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunocytochemistry applications. It has been designed to recognize GABRA1 from human, rat, and mouse samples.
Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG) is directly labeled with an ATTO-488 fluorescent dye. ATTO dyes are characterized by strong absorption (high extinction coefficient), high fluorescence quantum yield, and high photo-stability. The ATTO-488 label is analogous to the well known dye fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and can be used with filters typically used to detect FITC. Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody has been tested in immunohistochemistry and live cell imaging applications and is especially suited for experiments requiring simultaneous labeling of different markers.
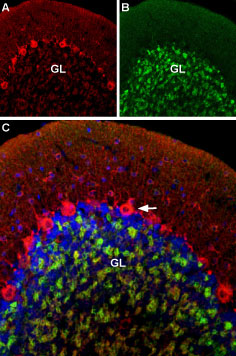
Multiplex staining of CaV1.2 and GABA(A) α1 Receptor in rat cerebellumImmunohistochemical staining of rat cerebellum using Guinea pig Anti-CaV1.2 (CACNA1C) Antibody (#ACC-003-GP) and Anti-GABA(A) α1 Receptor (extracellular)-ATTO Fluor-488 Antibody (#AGA-001-AG). A. CaV1.2 (red) is detected mostly in Purkinje cells (arrow). B. In the same section, GABRA1 (green) is observed in the granule layer. C. Merge of the two images suggests some colocalization between CaV1.2 and GABRA1 in the rat granule layer, but only CaV1.2 appears in Purkinje cells.
Applications
Citations
- Rat primary hippocampal neurons.
Sarto-Jackson, I. et al. (2012) J. Biol. Chem. 287, 14201.
