Overview
Cat #:
C-125
Alternative Name (E)-Capsaicin, CPS
Lyophilized Powder yes
Source Synthetic
MW: 305.4
Purity: >98% (HPLC)
Effective concentration 0.1-10 μM.
Chemical name (E)-N-[(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-8-methyl-6-nonenamide.
Molecular formula C18H27NO3.
CAS No.: 404-86-4
Activity Capsaicin is one of the most powerful chemical agonists of the TRPV1 (transient receptor potential vanilloid) channel. It is a small lipophilic molecule derived from hot chili peppers that acts on sensory neurons by opening TRPV1, a principal transduction channel for nociception1. Capsaicin acts directly on TRPV12, with half-maximal effective concentration of 711.9 nM in Xenopus oocytes3 and 0.29 μM in HEK293 cells4.
References-Activity
- Li, H. et al. (2011) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 8497.
- Vriens, J. et al. (2009) Mol. Pharmacol. 75, 1262.
- Caterina, M.J. et al. (1997) Nature 389, 816.
- McNamara, F.N. et al. (2005) Br. J. Pharmacol. 144, 781.
Shipping and storage Shipped at room temperature. Product as supplied can be stored intact at room temperature for several weeks. For longer periods, it should be stored at -20°C.
Solubility Ethanol. Centrifuge all product preparations before use (10000 x g 5 min).
Storage of solutions Up to one week at 4°C or six months at -20°C.
Our bioassay
 Alomone Labs Capsaicin activates TRPV1 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of TRPV1 currents, reversibly activated in a concentration dependent manner by 0.5 µM and 2.5 µM Capsaicin (#C-125) while membrane potential was held at -80 mV.
Alomone Labs Capsaicin activates TRPV1 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes.Time course of TRPV1 currents, reversibly activated in a concentration dependent manner by 0.5 µM and 2.5 µM Capsaicin (#C-125) while membrane potential was held at -80 mV. Alomone Labs Capsaicin induces Ca2+ influx via activation of TRPV1 channels expressed in C6 cells.Cells were loaded with Fluo-3 AM and stimulated with Capsaicin (#C-125). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ were detected via changes in Fluo-3 emission following application. The left panel shows normalized fluorescence before and after application, at 20 seconds, of 0-10 µM Capsaicin (as indicated). The right panel shows normalized fluorescence plotted against Capsaicin concentrations.
Alomone Labs Capsaicin induces Ca2+ influx via activation of TRPV1 channels expressed in C6 cells.Cells were loaded with Fluo-3 AM and stimulated with Capsaicin (#C-125). Changes in intracellular Ca2+ were detected via changes in Fluo-3 emission following application. The left panel shows normalized fluorescence before and after application, at 20 seconds, of 0-10 µM Capsaicin (as indicated). The right panel shows normalized fluorescence plotted against Capsaicin concentrations.
References - Scientific background
- Caterina, M.J. et al. (1997) Nature 389, 816.
- Tominaga, M. et al. (1998) Neuron 21, 531.
- Vriens, J. et al. (2009) Mol. Pharmacol. 75, 1262.
- Li, H. et al. (2011) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 8497.
- Jordt, S.E. and Julius, D. et al. (2002) Cell 108, 421.
- Jung, J. et al. (1999) J. Neurosci. 19, 529.
- McNamara, F.N. et al. (2005) Br. J. Pharmacol. 144, 781.
- Weltzin, M.M. and Schulte, M.K. et al. (2010) J. Pharmacol. 334, 917.
Scientific background
Vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1, TRPV1) is a nonselective cation channel that is activated by heat and acid, as well as vanilloids1,2.
Capsaicin is a TRPV1 agonist, which acts directly on TRPV13. Being small and hydrophobic, capsaicin crosses the plasma membrane readily to reach its intracellular ligand-binding site on TRPV1, leading to channel activation and cation permeation4-6.
Capsaicin acts directly on TRPV11, with half-maximal effective concentration of 711.9 nM in Xenopus oocytes3 and 0.29 µM in HEK293 cells7.
Target TRPV1 channels
Lyophilized Powder
Capsaicin (#C-125) is a highly pure, Synthetic, and biologically active compound.
Image & Title 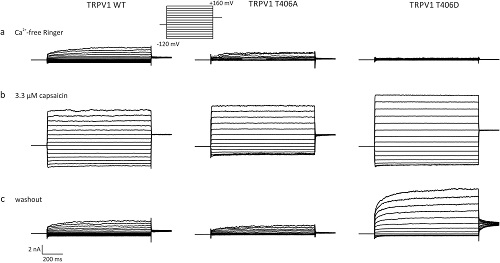
Alomone Labs Capsaicin activates TRPV1 in CHO transfected cells.Cells were transfected with wild type (WT) TRPV1 and different mutant forms of the channel. Voltage-dependence was measured by voltage-step protocol with depolarizing pulses from −120 mV to +160 mV. A. In a Ca2+-free solution, voltage-dependent currents are measured in WT and T406A mutant. B. Application of 3.3 μM Capsaicin (#C-125) induces robust voltage-dependent currents in CHO cells expressing TRPV1. C. Voltage-activated currents one minute after washout of Capsaicin shows an increased dependence of T406D mutant compared to WT and T406A which returned to baseline.Adapted from Jendryke, T. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 22007. with permission of NATURE SPRINGER.

Alomone Labs Capsaicin activates TRPV1 in CHO transfected cells.Cells were transfected with wild type (WT) TRPV1 and different mutant forms of the channel. Voltage-dependence was measured by voltage-step protocol with depolarizing pulses from −120 mV to +160 mV. A. In a Ca2+-free solution, voltage-dependent currents are measured in WT and T406A mutant. B. Application of 3.3 μM Capsaicin (#C-125) induces robust voltage-dependent currents in CHO cells expressing TRPV1. C. Voltage-activated currents one minute after washout of Capsaicin shows an increased dependence of T406D mutant compared to WT and T406A which returned to baseline.Adapted from Jendryke, T. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 22007. with permission of NATURE SPRINGER.
For research purposes only, not for human use
Last Update: 08/05/2024
Applications
Citations
Citations
Product citations
- Jendryke, T. et al. (2016) Sci. Rep. 6, 22007.
- Silva, M. et al. (2016) Neuropharmacology 107, 49.

